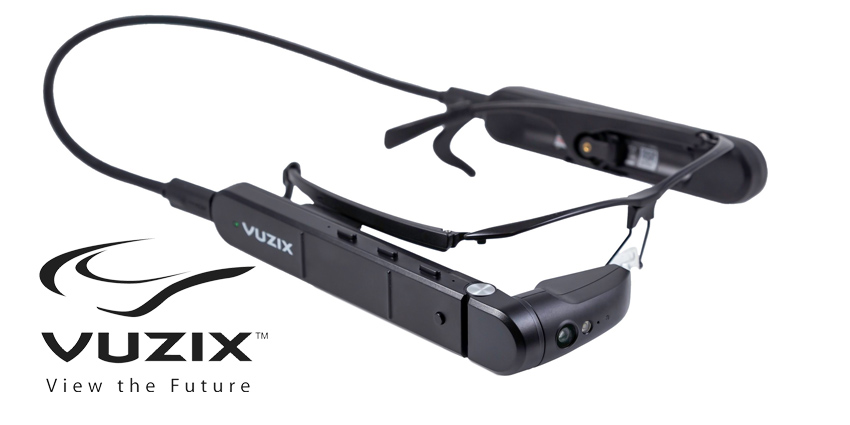
The promise of Augmented Reality (AR) in the enterprise has long been a compelling vision: a future where frontline workers have digital information seamlessly overlaid onto their physical world, boosting efficiency, accuracy, and safety. For years, however, this vision was hampered by a significant bottleneck—the complex, costly, and time-consuming process of creating AR content. Developing applications for smart glasses traditionally required teams of specialized programmers, long development cycles, and substantial investment, placing it out of reach for many organizations. Today, a paradigm shift is underway, driven by the convergence of increasingly powerful hardware and a new generation of no-code and low-code Extended Reality (XR) platforms. This movement is democratizing AR content creation, empowering subject matter experts without any coding knowledge to build and deploy sophisticated solutions. This article explores this pivotal trend in Smart Glasses News, delving into the technology, its real-world applications, and the profound impact it’s having on industries from manufacturing to defense.
The Foundation: Advanced Hardware Meets Accessible Software
The current explosion in enterprise AR adoption is not the result of a single breakthrough but rather the maturation and convergence of two critical domains: the smart glasses themselves and the software platforms that power them. One could not thrive without the other. We are witnessing a perfect storm where sophisticated wearable technology is finally being matched by software tools that make its power accessible to the masses.
The Evolution of Smart Glasses Hardware
Early smart glasses were often bulky, with limited battery life, narrow fields of view, and underpowered processors. They were fascinating prototypes but impractical for all-day use in demanding industrial environments. The latest Wearables News highlights a different story. Modern enterprise smart glasses are sleeker, more durable, and packed with technology. They feature high-resolution, see-through waveguide displays that project crisp images without obstructing the user’s view. Onboard System-on-Chip (SoC) architectures provide the processing power needed for complex tasks, a crucial aspect of AI Edge Devices News. This on-device processing allows for real-time analysis and decision-making without constant reliance on the cloud. Furthermore, a sophisticated array of sensors—including accelerometers, gyroscopes, and high-fidelity cameras—enables precise spatial tracking and environmental awareness. This sensor fusion is a hot topic in AI Sensors & IoT News, as it forms the basis for stable and convincing AR experiences. The integration of powerful, AI-driven computer vision, a key theme in AI-enabled Cameras & Vision News, allows these devices to recognize objects, text, and barcodes in the user’s environment, turning the glasses from a simple display into an intelligent, context-aware tool.
The Software Bottleneck: From Custom Code to No-Code Platforms
While the hardware was advancing, the software side lagged, creating a significant barrier to entry. Developing an AR application required proficiency in programming languages like C# or C++ and expertise with complex game engines like Unity or Unreal. This meant that an engineer who wanted to create a simple AR-guided maintenance procedure had to translate their knowledge for a software developer, leading to a slow, expensive, and often inaccurate development cycle. The rise of no-code XR platforms changes this dynamic entirely. These platforms abstract away the underlying code, providing a visual, drag-and-drop interface. This shift is a major story in AI Tools for Creators News, empowering a new class of creator: the subject matter expert (SME). A maintenance supervisor, a logistics manager, or a training instructor can now directly build the AR experiences they need, using their deep domain knowledge to create practical, effective tools without writing a single line of code. This democratization is the key catalyst unlocking the widespread adoption of smart glasses in the enterprise.
Under the Hood: Deconstructing No-Code AR Creation
To appreciate the power of these platforms, it’s essential to understand their core components and how they work together to translate a user’s intention into a functional AR experience. These platforms are sophisticated systems designed to handle everything from asset management to deployment on a global scale.

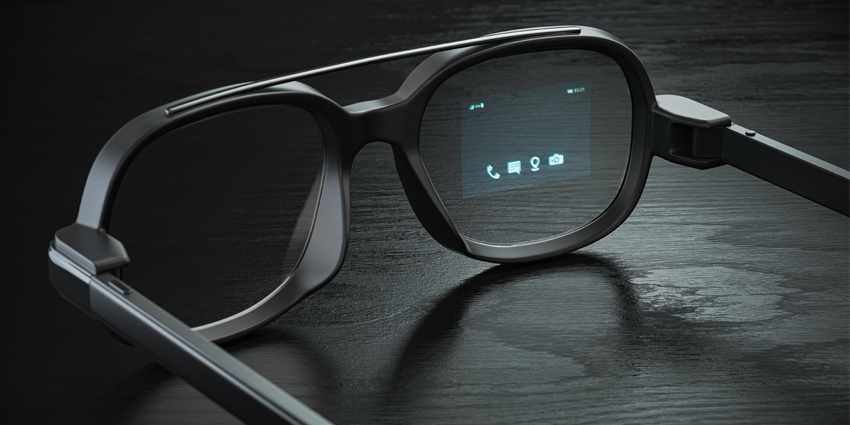
The Core Components of a No-Code Platform
At its heart, a typical no-code XR platform consists of several key integrated systems. First is a cloud-based Content Management System (CMS), which acts as a central repository for all digital assets. Users can upload 3D models (in formats like .glTF, .FBX), instructional videos, images, audio clips, and PDF documents. The platform often includes tools for asset optimization, automatically compressing and converting files for optimal performance on the target smart glasses. The second major component is the Visual Workflow Editor. This is the “no-code” magic, where users define the logic of the application. Using a simple drag-and-drop or flowchart-style interface, an SME can create a sequence of steps, such as: “When the user scans the QR code on Pump A, display the 3D model of its impeller and play the ‘Safety Shutdown’ video.” Finally, a powerful Publishing and Deployment Engine allows administrators to push the completed AR experiences over-the-air to an entire fleet of devices, manage user permissions, and update content remotely.
Triggering and Anchoring Content in the Real World
An AR experience is only useful if its digital content appears in the right place at the right time. No-code platforms provide a variety of methods to “trigger” and “anchor” this content. The most common method is marker-based tracking, where the device’s camera recognizes a specific QR code, barcode, or custom image to launch a related experience. More advanced platforms leverage AI-powered object recognition, a highlight of recent AI-enabled Cameras & Vision News, allowing the glasses to identify a specific piece of machinery or a component part without a marker. For experiences that need to exist in a general space, platforms use Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) technology to create a 3D map of the environment, enabling users to place and anchor digital content to fixed points in physical space. This data-driven approach to content delivery is also a key feature of the broader AR/VR AI Gadgets News landscape.
From Theory to Practice: No-Code AR in Action
The true measure of this technology is its impact on the ground. Across various industries, no-code AR is moving from a futuristic concept to a practical tool that solves real-world problems and delivers a tangible return on investment.
Manufacturing and Assembly
Consider a complex assembly line where workers must follow intricate, multi-step procedures. Traditionally, this involves consulting paper manuals or a nearby computer terminal, leading to inefficiencies and potential errors. With a no-code AR solution, a line manager can create a guided workflow. A new worker wearing smart glasses can look at a specific workstation, and the device will automatically recognize it, overlaying digital instructions, highlighting the correct parts bin, and showing an animated 3D model of the next assembly step. This hands-free guidance reduces cognitive load, minimizes errors, and dramatically shortens training time. It effectively transforms the factory floor into a more dynamic and data-rich environment, a trend also seen in AI Office Devices News as technology reshapes workspaces.
Field Service and Maintenance
In field service, technicians are often dispatched to remote locations to repair unfamiliar or highly complex equipment. A no-code platform allows an experienced engineer at headquarters to create a detailed AR-guided repair manual. The field technician arrives on-site, scans a serial number on the machine, and their smart glasses immediately display step-by-step troubleshooting procedures, safety warnings, and schematics. If they encounter an unexpected issue, they can initiate a “see-what-I-see” video call, where a remote expert can view their live feed and draw annotations that appear anchored in the technician’s real-world view. This capability drastically improves first-time fix rates, enhances safety, and leverages expert knowledge across a wider geographical area. It also integrates data from AI Monitoring Devices News, allowing technicians to see real-time sensor readings from the equipment they are servicing.

Defense and Logistics
In the defense and aerospace sectors, precision and accuracy are paramount. No-code AR is being used to create sophisticated training and operational support tools. For example, a maintenance crew can be guided through a pre-flight inspection of an aircraft, with the smart glasses automatically verifying each checkpoint and logging the results. In logistics, warehouse workers can be guided through a massive facility with navigational overlays, and item-picking instructions are displayed directly in their line of sight, enabling hands-free operation and improving pick-and-pack speeds. This intersects with trends in Autonomous Vehicles News, where human workers and robotic systems collaborate in smart warehouses. The ability to provide secure, context-aware information on demand is also a significant advancement for AI Security Gadgets News in secure environments.
Navigating the Path to Adoption: Considerations and Future Trends
While the benefits are clear, successful implementation requires careful planning and an awareness of both the technology’s limitations and its future trajectory. Adopting this technology is not just about buying hardware; it’s about rethinking workflows.
Best Practices for Implementation
Organizations looking to deploy AR should start with a well-defined pilot project that addresses a specific, high-value pain point. This proves the concept and builds momentum for a wider rollout. It is critical to involve the end-users—the technicians, operators, and trainers—in the content creation process from day one. Since they are the subject matter experts, their involvement ensures the final product is practical and useful. Finally, scalability is key. Choose a platform that can integrate with existing enterprise systems (like ERP or LMS) and provides robust tools for managing a large and geographically dispersed fleet of devices.

Common Pitfalls and Challenges
Despite significant advances, challenges remain. Hardware limitations such as battery life for a full work shift and the field of view of the display are still key considerations. Another common pitfall is underestimating the importance of content quality. “No-code” simplifies the creation *process*, but it doesn’t automatically create high-quality 3D models, clear videos, or well-written instructions. A “garbage in, garbage out” principle applies. Furthermore, organizations must plan for change management to overcome potential user resistance and effectively integrate these new digital workflows into established operational procedures.
The Future is AI-Driven
Looking ahead, the integration of more advanced AI will make these platforms even more powerful. We are on the cusp of generative AI models that can create 3D assets from simple text descriptions, further simplifying content creation. The next wave of AI Assistants News points to conversational AI agents integrated into the glasses, allowing users to ask questions and receive guidance in natural language. In the long term, advancements in Neural Interfaces News could offer even more intuitive ways to control and interact with digital content. This fusion of AR and AI will create a truly intelligent and proactive assistant that not only displays information but anticipates the user’s needs.
Conclusion: A New Industrial Reality
The convergence of powerful, lightweight smart glasses and intuitive, no-code XR software platforms represents a watershed moment for enterprise and industrial technology. This powerful combination is finally breaking down the barriers that have long relegated AR to pilot projects and research labs. By placing the power of content creation directly into the hands of subject matter experts, organizations can now rapidly develop and deploy solutions that enhance productivity, improve safety, and close skills gaps. This democratization is accelerating ROI and proving the value of AR in the most demanding environments. As a pivotal topic in AR/VR AI Gadgets News, this trend is not merely an incremental improvement; it is a fundamental shift in how the human workforce will interact with digital information, bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds to create a smarter, more connected industrial reality.