Once relegated to the realm of hobbyists and aerial photographers, drones have undergone a profound transformation. The integration of artificial intelligence has elevated these unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) from remote-controlled tools into intelligent, autonomous agents capable of complex decision-making. This fusion of robotics and machine learning is unlocking unprecedented applications that are reshaping entire industries, from public safety and infrastructure management to retail and logistics. As we delve into the latest in Drones & AI News, it’s clear we are witnessing the dawn of a new era where drones can see, think, and act on their own, presenting both immense opportunities and significant challenges. This article explores the technological underpinnings of this revolution, examines groundbreaking real-world applications, and navigates the critical technical and ethical considerations that will shape the future of autonomous aerial systems.
The Synergy of Silicon and Sky: Unpacking AI-Powered Drone Technology
The leap from manually piloted drones to fully autonomous systems is powered by a sophisticated convergence of AI disciplines, advanced sensor technology, and powerful onboard computing. This synergy creates a closed loop of perception, processing, and action, allowing the drone to operate intelligently within dynamic environments. Understanding these core components is essential to appreciating the scope of their current and future capabilities.
The AI Brain: Advanced Computer Vision and Machine Learning
At the heart of an intelligent drone is its ability to perceive and interpret the world visually. This is where AI, specifically computer vision, plays the starring role. Modern drones are equipped with high-resolution cameras, but it’s the AI software that turns a simple video stream into actionable intelligence. Algorithms for object detection and classification enable a drone to identify specific items, people, or vehicles. For instance, in an agricultural setting, a drone can distinguish between healthy crops, weeds, and signs of pest infestation. In security applications, it can identify a person loitering in a restricted area or a vehicle that doesn’t belong. This capability is central to the latest AI-enabled Cameras & Vision News, where the focus is shifting from mere image capture to real-time environmental understanding.
The Autonomous Body: Superior Navigation and Flight Control
True autonomy requires more than just seeing; it demands the ability to navigate complex, unpredictable spaces without human intervention. This is achieved through a combination of sensor fusion and advanced algorithms like SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping). Using data from GPS, LiDAR, inertial measurement units (IMUs), and visual cameras, the drone builds a real-time map of its surroundings and simultaneously determines its position within that map. This technology, closely related to developments in Autonomous Vehicles News, allows drones to avoid obstacles, from trees and buildings to other moving objects, and to execute complex flight paths with precision. This is a critical component for applications like indoor inventory management or navigating dense urban canyons for package delivery.
From Raw Data to Real-Time Action
The final piece of the puzzle is the drone’s ability to process information and make decisions on the fly. The rise of powerful, low-energy processors has made it possible to run complex AI models directly on the drone, a trend highlighted in AI Edge Devices News. This “edge computing” minimizes latency by eliminating the need to send data to a cloud server for analysis. A security drone can therefore detect a threat, decide on a course of action (e.g., follow, illuminate, alert), and execute it in milliseconds. This transition from being a simple data collection platform to an active participant in a workflow is what truly defines the modern AI-powered drone.
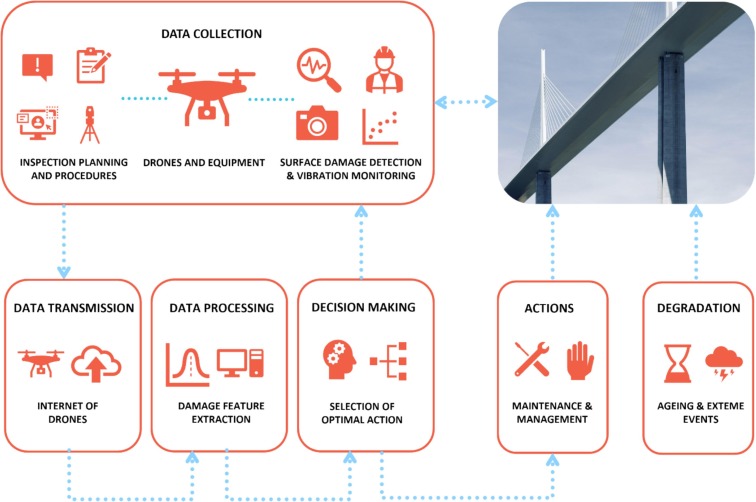
From Theory to Reality: Groundbreaking Applications of AI Drones
The theoretical capabilities of AI drones are now being translated into tangible, high-impact solutions across various sectors. These applications demonstrate a clear shift from passive monitoring to active, intelligent intervention, solving complex problems with unprecedented efficiency and safety. While some applications are widely celebrated, others push the boundaries of social acceptance and regulation.
The New Frontier of Asset Protection and Retail Security
One of the most talked-about, and controversial, applications is in the realm of security. Imagine a large retail distribution center or a big-box store where traditional security cameras have blind spots. According to the latest AI Security Gadgets News, integrated systems are being developed where AI-powered cameras detect suspicious activity, such as a potential shoplifter concealing an item. Instead of merely recording the event, the system automatically dispatches an autonomous drone from a docking station. The drone, navigating safely indoors, can then track the individual, keeping them in clear view, recording high-definition evidence, and streaming the video feed to security personnel’s mobile devices. This provides an undeniable record of events and acts as a powerful deterrent. The drone wouldn’t engage physically but would serve as a persistent, mobile witness, ensuring that security can respond effectively and with full situational awareness. This represents a paradigm shift in loss prevention, moving from reactive analysis to proactive, real-time response.
Revolutionizing Infrastructure Inspection and Maintenance
A less controversial but equally transformative application is in the inspection of critical infrastructure. Manually inspecting miles of power lines, vast bridges, or towering wind turbines is dangerous, time-consuming, and expensive. AI-powered drones automate this process with incredible precision. Equipped with thermal and high-resolution cameras, a drone can fly a pre-programmed route, capturing thousands of images. The onboard AI or a cloud-based platform then analyzes this data to detect minute signs of wear and tear—such as hairline cracks in concrete, corrosion on steel, or overheating components on a power line. This proactive maintenance, a key topic in Smart City / Infrastructure AI Gadgets News, prevents catastrophic failures, saves millions in repair costs, and, most importantly, keeps human inspectors out of harm’s way.
Enhancing Emergency Response and Disaster Management
In the chaotic aftermath of a natural disaster, information is the most valuable resource. AI drones are becoming indispensable tools for first responders. In a search-and-rescue operation following an earthquake, a fleet of drones can quickly map the affected area. Using thermal imaging and AI-driven pattern recognition, they can identify heat signatures that may indicate a survivor trapped in rubble, a task far faster than a ground team could perform. In firefighting, drones provide a crucial aerial perspective, using AI to track the fire’s spread, identify hotspots, and help commanders allocate resources more effectively. This application of AI Monitoring Devices News showcases how technology can be a powerful force for good, directly contributing to saving lives.
Navigating the Turbulent Skies: Technical and Ethical Hurdles
Despite the immense potential, the widespread adoption of autonomous AI drones faces significant obstacles. These challenges are not just technical but also deeply rooted in regulatory frameworks and societal concerns about privacy and control. Addressing these issues responsibly is paramount for the sustainable growth of the industry.
The Triad of Limitations: Battery, Bandwidth, and Onboard Brains
The laws of physics and engineering still impose practical limits. Battery life remains a primary constraint, with most commercial drones offering flight times of 30-45 minutes. This necessitates solutions like autonomous docking and charging stations for persistent operations. Secondly, while edge computing is powerful, the most complex AI analysis still often requires cloud processing, which depends on a stable, high-bandwidth connection like 5G. In remote areas or disaster zones, this connectivity can be unreliable. Finally, the processing power of AI Edge Devices News is constantly improving, but there’s always a trade-off between a drone’s size, weight, power consumption, and its computational capabilities.
The Regulatory Labyrinth
Aviation authorities worldwide, like the FAA in the United States, are cautiously adapting regulations to accommodate autonomous drones. Rules governing Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) operations—essential for applications like long-range inspection or package delivery—are complex and often require special waivers. Ensuring that an autonomous drone can safely share the airspace with manned aircraft, navigate populated areas without risk, and have foolproof fail-safes is a monumental regulatory challenge. Companies must invest heavily in compliance and proving the safety of their systems.
The Privacy and Surveillance Predicament
Perhaps the most significant barrier to public acceptance is the issue of privacy. The idea of autonomous drones flying overhead, equipped with high-resolution cameras and AI capable of facial recognition and behavior analysis, raises legitimate fears of a surveillance society. How is the collected data stored and secured? Who has access to it? What prevents its misuse? These questions, echoed in discussions around AI Personal Robots News and smart home devices, are even more acute for mobile, aerial platforms. Building public trust will require transparent policies, strong data encryption, clear regulations on what can be recorded, and robust ethical guidelines for operators.
Best Practices and the Future Outlook
For organizations looking to harness the power of AI drones, a strategic and responsible approach is crucial. The future of this technology will be defined not just by innovation, but by how well we integrate it into our society.
Tips for Responsible Implementation
- Start with a Defined Use Case: Don’t adopt drones for the sake of technology. Identify a specific, high-value problem that an autonomous aerial solution can solve more efficiently or safely than current methods.
- Prioritize Safety and Compliance: Work closely with regulatory bodies from the outset. Invest in rigorous testing, pilot training (even for autonomous systems), and robust hardware with multiple redundancies.
- Develop a Data Governance Framework: Be transparent about what data is being collected and why. Implement strong security protocols to protect that data from breaches and ensure it is used only for its intended purpose.
- Engage in Community Outreach: For public-facing applications, proactively engage with the community to explain the benefits of the technology and address concerns about noise, safety, and privacy head-on.
The Road Ahead: Swarms, Miniaturization, and Deeper Integration
The trajectory of Drones & AI News points toward an even more integrated and intelligent future. We will see the rise of drone “swarms,” where multiple drones collaborate on a single task, like mapping a large area or providing 3D security coverage of a major event. Advances in materials and battery technology will lead to smaller, quieter, and more agile drones capable of longer flight times. Ultimately, drones will become just one type of node in a larger, interconnected ecosystem of AI Sensors & IoT News, seamlessly sharing data with smart city infrastructure, autonomous ground vehicles, and central AI command systems to create a truly responsive and intelligent environment.
Conclusion: Charting a Course for Responsible Aerial Autonomy
The fusion of artificial intelligence and drone technology is undeniably one of the most exciting frontiers in robotics today. From enhancing security and optimizing logistics to saving lives in emergencies, the benefits are compelling and tangible. However, this powerful technology brings with it a profound responsibility. The path to widespread adoption is paved with challenges—technical limitations, complex regulations, and critical ethical questions about privacy and surveillance. The success of this revolution will hinge not only on continued technological innovation but on our collective ability to build a framework of trust, transparency, and accountability. As the autonomous eye in the sky becomes more common, we must ensure it serves to uplift and protect society, not simply to watch over it.





