Introduction: The Dawn of the Autonomous Home
For decades, science fiction has promised us a future where domestic life is managed by intelligent, autonomous machines. From the animated antics of The Jetsons to the helpful droids of Star Wars, the concept of a robotic companion has been etched into our cultural consciousness. Today, that fiction is rapidly hardening into fact. As major technology conglomerates pivot their R&D focus from saturated markets like electric vehicles and smartphones toward the next big hardware innovation, AI Personal Robots News is dominating the headlines. We are witnessing a seismic shift in consumer electronics, moving from static smart speakers to mobile, context-aware entities that can navigate our homes, understand our needs, and interact with us on a human level.
This transition is not merely about putting wheels on a tablet. It represents the convergence of advanced robotics, computer vision, and the explosive growth of Large Language Models (LLMs). The industry is exploring diverse form factors, ranging from mobile rovers that follow you from room to room, to sophisticated table-top devices with actuating displays that mimic human head movements. As we delve into Smart Home AI News, it becomes clear that the race is on to define the “iPhone moment” for robotics—a device that seamlessly integrates into daily life, offering utility, companionship, and enhanced security without feeling intrusive.
Section 1: The Evolution from Smart Speakers to Intelligent Agents
The Limitations of Static AI
For the past decade, the smart home has been anchored by stationary devices. Smart speakers and displays served as the central nervous system, controlling lights, locks, and thermostats. However, their utility is limited by their immobility. If you are in the kitchen and the smart display is in the living room, the connection is severed. AI Assistants News suggests that consumers are looking for continuity. The industry’s answer is mobility. By liberating the AI from a fixed point, technology companies are creating agents that can maintain context, presence, and utility wherever the user goes.
Form Factors: Mobile Rovers vs. Table-Top Actuators
Current explorations in Robotics News reveal two primary design philosophies emerging from hardware engineering labs. The first is the “mobile rover.” These are autonomous units equipped with LiDAR and optical sensors, capable of mapping a home and navigating dynamic obstacles (like pets or discarded toys). They serve as mobile videoconferencing units, security patrols, and moving media centers.
The second philosophy focuses on “table-top robotics.” Imagine a smart display attached to a sophisticated robotic arm. This device isn’t mobile in the sense of moving across the floor, but it possesses “social movement.” It can pan, tilt, and rotate to face the user, mimicking eye contact and engagement. This aligns with AI Companion Devices News, where the goal is to create a hardware interface that feels less like a computer and more like a present, attentive entity. This distinction is crucial: one solves the problem of “being there” (mobility), while the other solves the problem of “connection” (interaction).
The Role of Generative AI
Hardware is only half the equation. The integration of Generative AI is what transforms these machines from remote-controlled toys into genuine assistants. AI Research / Prototypes News indicates that next-generation personal robots will not rely on rigid command-and-response scripts. Instead, they will utilize on-device LLMs to understand natural language, infer intent, and even perceive emotions. If a user sighs heavily, the robot might lower the lighting or play soothing music, bridging the gap between AI Audio / Speakers News and emotional intelligence.
Section 2: Technical Breakdown and Ecosystem Integration
Advanced Vision and Navigation

To operate safely in a cluttered home environment, personal robots require enterprise-grade perception stacks. This is where AI-enabled Cameras & Vision News becomes critical. These devices utilize V-SLAM (Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) to create real-time 3D maps of the environment. Unlike the basic mapping found in Robotics Vacuum News, these systems must identify specific objects—differentiating between a dropped sock and a pet—and understand semantic context (e.g., “Go to the kitchen” vs. “Come to the sofa”).
This level of processing requires immense compute power. To preserve privacy and reduce latency, much of this processing happens locally. AI Edge Devices News highlights the development of specialized neural processing units (NPUs) designed specifically for robotics. These chips handle the heavy lifting of computer vision and sensor fusion without constantly pinging the cloud, which is essential for user trust.
Integration with the IoT Fabric
A personal robot cannot exist in a vacuum; it must act as the conductor of the smart home orchestra. The synergy between AI Sensors & IoT News and robotics is profound. Consider the following integration scenarios:
- Smart Appliances: The robot communicates with Smart Appliances News protocols. It can visually inspect if the oven was left on or if the refrigerator door is ajar, sending a notification to your phone.
- Wearables: By syncing with Wearables News (smartwatches and fitness trackers), the robot can adjust its behavior based on your biometric data. If your watch detects high stress, the robot might suggest a meditation session.
- Security: In the realm of AI Security Gadgets News, a mobile robot acts as an active sentry. Unlike fixed cameras with blind spots, a robot can investigate a triggered window sensor, stream video to the homeowner, and even deter intruders via two-way audio.
The Table-Top Robotic Interface
Focusing on the table-top concept, the engineering challenges are unique. These devices often feature a display mounted on a thin robotic arm. The mechanics must be silent and smooth to avoid the “uncanny valley” effect. AI Phone & Mobile Devices News intersects here, as these devices often serve as docking stations or extensions of the smartphone experience. The screen must orient itself perfectly to the user’s gaze, utilizing face tracking similar to AI Cameras News found in high-end conference rooms. This creates a video calling experience that feels incredibly natural, as if the remote person is physically turning their head to look at you.
Section 3: Real-World Applications and Societal Impact
Revolutionizing Health and Eldercare
Perhaps the most compelling use case for personal robots lies in Health & BioAI Gadgets News. As the global population ages, the demand for “aging in place” technologies is skyrocketing. A personal robot can serve as a proactive health monitor. Through AI Monitoring Devices News, these robots can detect anomalies in gait, potentially predicting falls before they happen. If a fall occurs, the robot can autonomously navigate to the user, assess responsiveness, and contact emergency services.
Furthermore, for users with limited mobility, AI for Accessibility Devices News takes center stage. A robot that can fetch items, manipulate light switches, or simply provide a voice interface for the entire home can restore a significant degree of independence. This aligns with AI Sleep / Wellness Gadgets News, where the robot ensures the bedroom environment is optimized for rest, adjusting temperature and blackout shades automatically.
Education and Entertainment
In the living room, the personal robot transforms into an interactive hub. AI Toys & Entertainment Gadgets News suggests a future where robots are playmates and tutors. Utilizing AR/VR AI Gadgets News, a robot could project augmented reality games onto the floor or walls, turning a passive space into an immersive environment. For education, AI Education Gadgets News envisions robots that use Socratic methods to help children with homework, projecting diagrams or reading aloud with emotive intonation.
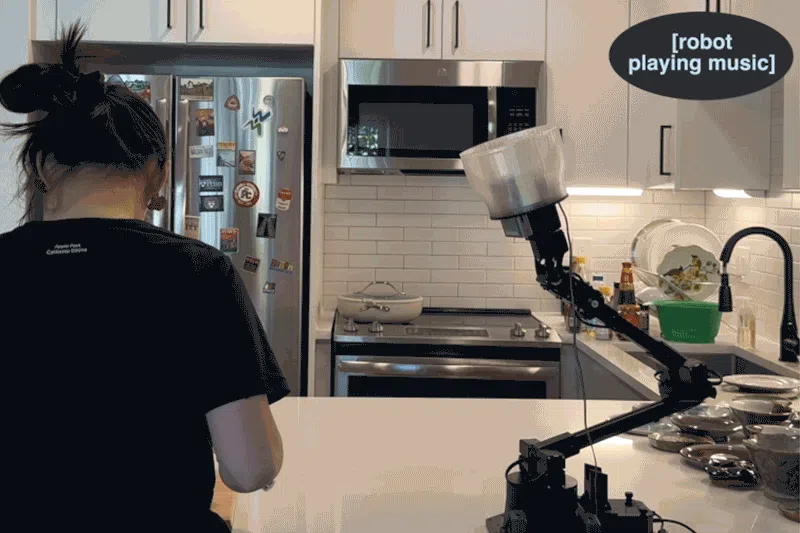
The “Butler” in the Kitchen
AI Kitchen Gadgets News is often focused on smart ovens, but a personal robot brings intelligence to the workflow. Imagine a device that projects a recipe onto the countertop (using pico-projectors), sets multiple timers based on voice commands, and uses computer vision to advise when a steak is perfectly seared. While we are not yet at the stage of a humanoid robot chopping vegetables, the table-top robotic assistant can act as the ultimate sous-chef, managing the logistics of cooking while the human handles the dexterity.

Case Study Scenario: The Morning Routine
To visualize the impact, consider a morning routine in 2026:
- 7:00 AM: Your AI Lighting Gadgets News integrated system simulates a sunrise. The personal robot, docked by the bed, wakes you with a weather summary.
- 7:15 AM: As you move to the kitchen, the robot follows (or hands off to a kitchen unit). It briefs you on your schedule, pulling data from AI Office Devices News integrations.
- 7:30 AM: You realize you’re out of coffee. The robot notes this and places an order via AI Tools for Creators News (commerce integration).
- 8:00 AM: You leave for work. The robot switches to “Sentry Mode,” patrolling the house and syncing with Drones & AI News (an indoor security drone) for a comprehensive sweep.
Section 4: Challenges, Privacy, and Future Considerations
The Privacy Paradox
The introduction of cameras and microphones that can move around the home raises significant privacy concerns. AI Security Gadgets News often highlights the tension between utility and surveillance. A robot that maps your home knows the layout of your private spaces, the location of your valuables, and your daily habits. Manufacturers must implement “Privacy by Design.” This includes physical camera shutters, local processing (keeping video off the cloud), and transparent data policies. The success of this category depends entirely on consumer trust.
Technical Hurdles and Cost
Robotics is hard. Unlike software, which can be patched over the air, hardware failures are costly. Motors burn out, gears strip, and batteries degrade. AI Research / Prototypes News shows that achieving the reliability of a refrigerator in a complex mobile robot is a massive engineering hurdle. Furthermore, cost is a barrier. To pack high-end mobile processors, LiDAR, high-resolution screens, and precision motors into a consumer device results in a high price tag. The industry must find the balance between premium features and mass-market accessibility.

The Uncanny Valley and Social Acceptance
Design plays a pivotal role. If a robot looks too human, it can be unsettling (the Uncanny Valley). If it looks too industrial, it feels cold. AI in Fashion / Wearable Tech News and industrial design trends suggest that the most successful home robots will likely adopt “soft robotics” aesthetics—using fabric meshes, rounded curves, and expressive but non-humanoid eyes to engender warmth without creeping out the user. This is crucial for AI Pet Tech News as well; the device must be accepted by household animals, not attacked by them.
Future Outlook: Beyond the Home
While the focus is currently on the home, the technology developed for personal robots has broader implications. Smart City / Infrastructure AI Gadgets News and AI for Energy / Utilities Gadgets News will benefit from the advancements in autonomous navigation and battery efficiency. We may see similar robotic principles applied to AI Gardening / Farming Gadgets News, where small autonomous units tend to backyard gardens, or AI for Travel Gadgets News, with robotic luggage that follows you through the airport.
Even Autonomous Vehicles News is tangentially related; the sensor stacks used in self-driving cars are essentially larger, more expensive versions of what is being fitted into home robots. As Neural Interfaces News advances, we might eventually control these robots via thought or subtle gestures, removing the friction of voice commands entirely.
Conclusion
The shift toward AI personal robots marks a pivotal moment in the history of consumer technology. We are moving beyond the era of passive screens into an era of active, physical agents. Whether through a mobile robot that patrols our halls or a table-top device that mimics human engagement, these machines promise to make our homes smarter, safer, and more connected. While challenges regarding privacy, cost, and social acceptance remain, the sheer momentum of investment from top-tier engineering divisions suggests that the robotic butler is no longer a fantasy.
As we digest the latest AI Personal Robots News, it is clear that the smart home is waking up. It is gaining eyes, ears, wheels, and—thanks to generative AI—a voice that understands us. For consumers, the future promises a blend of convenience and companionship, redefining what it means to live with technology.